While it’s important to have a website, it’s just as important to have a fast website.
Here are some interesting findings from a recent study by Econsultancy on the impact of website speed on commerce online:
- 47% of people expect a web page to load in two seconds or less
- 40% will abandon a web page if it takes more than three seconds to load
- 52% of online shoppers claim that quick page loads are important for their loyalty to a site
- 14% will start shopping at a different site if page loads are slow, 23% will stop shopping or even walk away from their computer
- 64% of shoppers who are dissatisfied with their site visit will go somewhere else to shop next time
- At peak traffic times, more than 75% of online consumers left for a competitor’s site rather than suffer delays
- 88% of online consumers are less likely to return to a site after a bad experience
- 1 second delay in site loading speed can cause 7% conversions loss
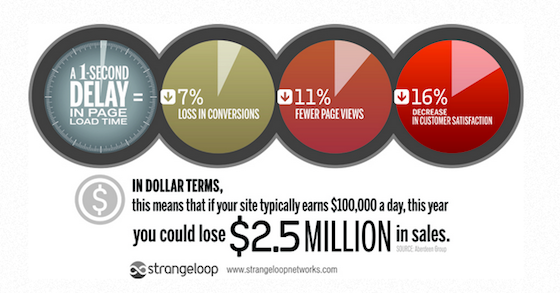
The above are just some of the interesting findings in the study and you can read the whole study here for more insights as well as a few tips.
While the above points are very revealing, it is also worth nothing that Google has officially announced that site speed is one of the factors it uses when it ranks website. With this said, not only could your slow website be costing you quality traffic from the search engines, it’s also probably costing you conversions. Here are a few tips to make your website faster:
1. Change Your Web Host
Your web hosting company will to a great extent determine how fast your website is; if you’re using a crappy web host, your website will be slow. If you’re using a web host not properly configured to work with your website platform, your website will be slow and your website will be slow if you’ve outgrown the capacity of your web host.
If your web host is not properly configured to power your website, all the other tips in this article won’t have much of an impact; so the first step is to get in touch with your web host to see if there’s something they can do to make your website faster and if you’re not satisfied with the results you get, change host.
Depending on how big your website is, what you need might be to get a better, bigger server; for example, you might need to upgrade from shared hosting to a VPS or dedicated server.
2. Limit the Number of Items on a Single Page of Your Website
It could be images, videos, links, comments or any other form of content on your website; the more content a visitor to your website can access at once, the more likely your website will be slow for them.
This is especially important if you use multimedia on your site, like images, as each image adds to the time it takes for your website to load thus making your website slower; you can make your website faster by having little content on each page of your website and giving people an option to click through to a next page to view the next page of content.
The potential this can have on site speed and user experience was effectively demonstrated in a 2009 Google study; Google experimented with displaying 30 results on a page as opposed to 10 and this led to an increase of 0.5 seconds in page load speed; it was noted that the pages that display 30 results experienced a 20% drop in traffic compared to the pages with just 10 results. We’re talking about a site load delay of less than 1 second here; in other words, even the small changes could have massive impact.
This also applies to those who have a blog; you can get more results by limiting the number of articles displayed on your blog homepage. Instead of having 10 – 20+ articles listed on one page, limit it to 3 – 5 and let people be able to click to access more content; this makes your site faster, drives more views and creates better user experience.
3. Don’t Host Your Files on Other Servers
This process is called “hotlinking” and it can be damaging to your website.
According to Wikipedia, hotlinking is “the practice of displaying an image on a website by linking to the same image on another website, rather than saving a copy of it on the website on which the image will be shown.” In other words, instead of downloading a version of an image you saw on Flickr and hosting it on your website, you decide to configure your website to pull the image directly from Flickr instead of your website whenever anyone visits the part of your website that has the image loaded; as a result, you’re saving bandwidth by relying on another person’s resources. The danger in this is that your website is relying on the third-party that hosts the image to run and if anything should happen to that site or the server, it’ll impact the portion of your website where the image is embedded.
To see how damaging hotlinking can be for your site speed, read this article by Steve to learn how hotlinking images on another server slowed down his ecommerce website and cost him sales for an entire day.
4. Optimize Images Used on Your Website
Images, if used effectively, can be very powerful for your website; in fact, a recent Poynter study has revealed that the bigger the image used with a piece of content, the more likely it is to draw people in to read the content.
In other words, the effectiveness of using images is undisputed; however, one thing is also very clear. The bigger the image used to support your content, the larger its size and the more likely it is to create a slow website experience for your users.
So how do you make your website fast while still using images? The answer is simple, optimize your images.
Most images are very big in size but the reality is that its not always the quality of an image that is taking up the space; a lot of factors come into place in this regards like useless colors, extra comments and unnecessary data stored in your image file. All these can be removed to significantly reduce the size of your image without reducing its quality and as a result make your website faster.
You can optimize your images before using them with your website by optimizing them with the Yahoo! Smush.it tool or by using a similar image optimizer.
5. Use a Content Delivery Network
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a collection of servers distributed in various locations with the aim of creating a better experience for people trying to access content hosted on these servers; in most cases, a CDN will have servers hosted in different countries and with your website hosted on the CDN, whenever someone tries to visit your website the CDN will automatically serve a version of your website hosted on their server in the location closest to them.
This can be very powerful if you get a lot of international traffic; since visitors can now access the version of your website closest to them, the amount of time it takes your website to load reduces significantly.
A great CDN network you can get started with is MaxCDN.









Thanks for the tips. I use WP Super Cache plugin and it has CDN inbuilt. CDN is a good concept to faster the site loading.